One person dies of melanoma every hour of every day in the United States. As if that statistic wasn’t sobering enough, the rates of melanoma have doubled
during the past three decades according to the Center for Disease Control (CDC). With over 7,000 people estimated to die of this vicious form of skin cancer in 2019, what can the average person do to decrease their risk?
Although we can’t avoid the sun altogether, we CAN be proactive in how we protect ourselves from its damaging rays. Luckily, some incredible advancements have been made in both sunscreen and antioxidant cosmetic chemistry to take your caliber of protection to the next level!
To better understand how we can prevent the occurrence of skin cancer, we first need to know what these potential cancers are. Let’s take a look at the three most commonly diagnosed skin cancers types.
Basal cell carcinoma
According to the American Cancer Society, of the more than 3 million cases of skin cancer diagnosed every year, more than 80 percent are basal cell carcinomas. This form of cancer tends to occur in areas of the body most frequently exposed to the sun, such as our face, ears, and neck. It is rare for this form of cancer to spread, but early detection is a must, as once diagnosed the incidence of reoccurrence increases.
Squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma accounts for around 20% of non-melanoma diagnosed skin cancers each year. Like basal cell carcinoma, it most frequently occurs in areas commonly exposed to the sun, but can also be found in other areas like scars, skin ulcers, hands, and the genital region. This type of skin cancer is slow growing and, like basal cell, rarely spreads.
Melanoma
The cells of our skin that produce pigment, or melanin, are known as melanocytes. Melanoma is a life-threatening cancer that forms these cells. Today, it is one of the most common cancers found among young adults, often as a result of tanning bed use. Melanoma is directly related to UV-induced skin damage; especially severe sunburns experienced from youth. Unlike basal and squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma is quick to spread and metastasize, making it especially dangerous if not caught early. Your best protection against melanoma is to avoid excessive sun exposure and vigilantly protect your skin when you are exposed.
The Relationship Between Sunscreen & Melanoma Prevention
In a 2011 randomized, clinical study of over 1,600 people, the Journal of Clinical Oncology found that regular use of a broad-spectrum UVA/UVB sunscreen reduced the incidence of melanoma by 50-73% when used as directed. UVB rays are shorter rays that the sun emits and are most likely to cause a burn, while UVA rays have a longer wavelength that penetrates the skin and causes advanced cellular damage that can lead to premature aging and cancer. Therefore, to truly have comprehensive protection, you need to wear a broad-spectrum UVA/UVB sunscreen.
Stepping Up Your Protections with an Antioxidant + Sunscreen Regimen
An exciting area of research and development surrounds the use of antioxidant serums to not only heighten our sun protection efforts but also repair the age-inducing damage generated from exposure. Antioxidants, such as Vitamin C and Ferulic Acid most often come in serum form to be more bio-available to our skin. These active ingredients prevent free radical damage from the sun by neutralizing them and inhibiting oxidation. Free radicals cause extensive DNA damage to our cells and can lead to mutations, such as cancer. As an added benefit, antioxidants also help prevent collagen and elastin loss and improve the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and pigmentation.
Antioxidants that Get an A+
A trifecta of vital antioxidants has risen to the top of the list of many skin care professionals in the last decade. These “All-Stars” are backed by promising clinical research and are shown to enhance not only your skin’s protection, but also its appearance.

Vitamin C
The most commonly known antioxidant, Vitamin C is celebrated for its ability to increase collagen production, prevent inflammation, brighten skin’s appearance, and even accentuate skin’s firmness.
Ferulic Acid
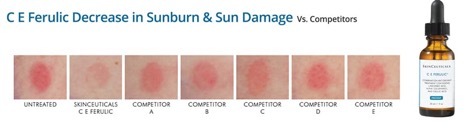
A study published in the International Journal of Nutrition, Pharmacology & Neurological Diseases found that ferulic acid, when topically applied to the skin, restored the viability of wounded dermal fibroblasts to 98%. The study exposed that dermal fibroblasts (skin cells essential to wound healing) with one-time exposure to UV rays had their viability reduced to 28%, but ferulic acid scavenged free radicals and destroyed them before they could damage cellular DNA. The study concluded that regular application of ferulic acid could dramatically reduce DNA mutations and damage leading to a reduction in the risk of skin cancer.
Phloretin
Research has found that phloretin, most commonly derived from apples, not only has antioxidant properties but can also interrupt melanin synthesis. This ability allows it to reduce skin discoloration caused by the sun dramatically. Phloretin also inhibits the formation of MMP-1 (matrix metalloproteinase), which breaks down collagen in our skin, making it a valuable anti-aging ingredient.
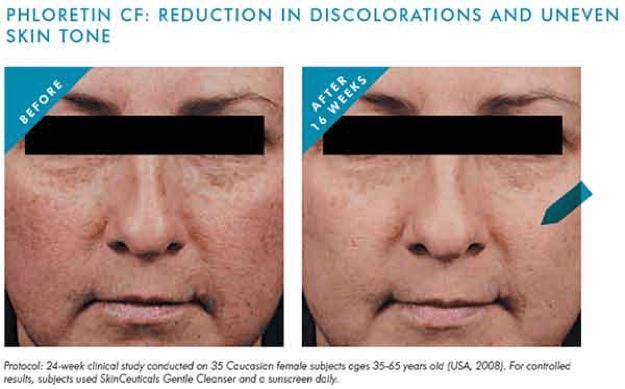
As you can see, there are marked benefits to combining the power of BOTH an antioxidant serum and a daily sunscreen to prevent and reduce the risk of skin cancer. Plus—you’ll be preventing premature aging and keeping your skin looking radiant and youthful for years to come!
Curious about what combination of antioxidant and sunscreen is best for you this Summer? Schedule a complimentary consultation with a Skin Artisan’s Licensed Esthetician to get matched with the perfect solution for your skin type and skin condition